One of the crucial link-building strategies is to create internal links.
Internal linking is one of the essential aspects of on-page optimization, yet it is often overlooked or misunderstood. It links one page to another page within your website.
While the concept may be simple, the implications are not. Internal linking is a powerful tool to influence your site architecture, content, and SEO. It can help your website rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), improve usability, and increase traffic and conversions when used correctly.
However, before using internal linking for SEO, it’s essential to understand its role in your website.
What are Internal Links?

Internal links work by connecting two pages on the same website. Internal links help visitors navigate a website and find the information they’re looking for.
By creating internal links pointing between web pages on your site, you can help to improve your ranking and help search engines index your site.
An internal link audit analyses your website’s internal linking structure to identify potential issues. Internal link analysis can be beneficial if you’ve recently changed your site structure or content.
Google Analytics is a tool that understands how people interact with your website. One of its powerful features is its ability to track internal links. By tracking clicks and pageviews, you can get a sense of what people are interested in and where they’re coming from.
However, an internal link structure uses different types of links.
HTML link
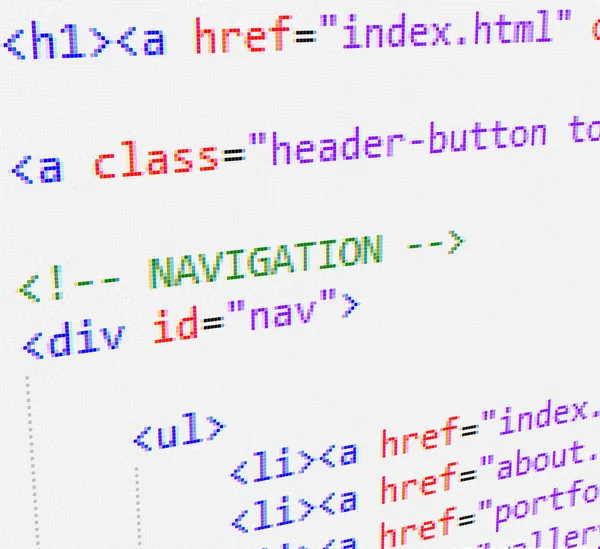
These are the links you see in a web page’s code to link to other pages on the same website. Most internal links use HTML links because they link pages on the same domain.
HTML links are created using the <a> element. The href attribute identifies the URL of the page the link will take you to.
Redirect Link
A redirect link is a link that automatically takes you to another page. Redirects send visitors from one URL to another, such as when a page has been moved or renamed.
They add links as redirection from the old URL to the new one. Creating shortcuts to high authority pages also uses redirect links.
Image link
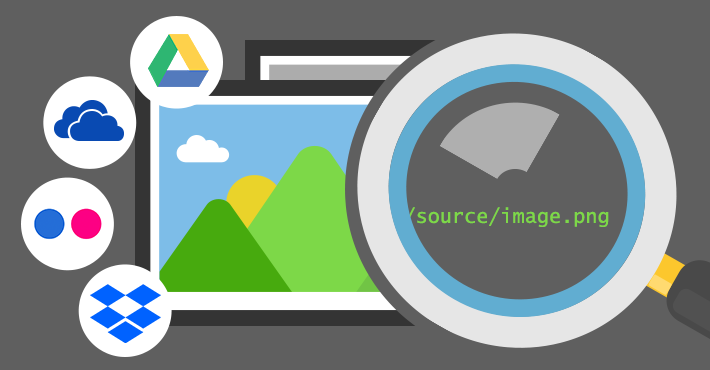
Image links link to other pages using an image instead of text.
The hyperlink links an image to another web page or file. When clicked, the image will open the linked content in a new window or tab.
Image links usually open more extensive versions of images or create a gallery of images.
What is the difference of Internal Link and External Link?
Internal links and external links are fundamental components of a website’s linking structure, influencing its functionality and search engine visibility. Let’s explore their differences and delve into the significance of internal links, while also providing a reference to external link building.
Internal Links:
Internal links are connections between pages within the same website. They contribute to the site’s architecture, allowing users to navigate seamlessly from one page to another. Internal links work like pathways, guiding visitors to relevant content and enhancing their overall experience.
The right internal linking strategy involves adding links contextually within the content. These links should be relevant, providing additional information or guiding the user to related pages. It’s crucial to avoid overloading a page with internal links, as this can dilute their value. Too many links may confuse visitors and dilute the link value.
External Links:
External links, on the other hand, connect pages on one website to pages on another. They play a significant role in search engine rankings, as search engines view external links as indications of a site’s credibility and authority. You can learn more about external link building and its importance here.
External links are like endorsements from one website to another. When valuable links from reputable sources point to a page on your site, it can positively impact your search engine rankings. However, it’s crucial to focus on quality over quantity. Valuable links from authoritative sites carry more weight than a multitude of links from less reputable sources.
Remember, whether it’s internal or external links, the key is to maintain a balance, keeping the user experience in mind while building a robust and authoritative web presence.
Types of Internal Links
Navigational links
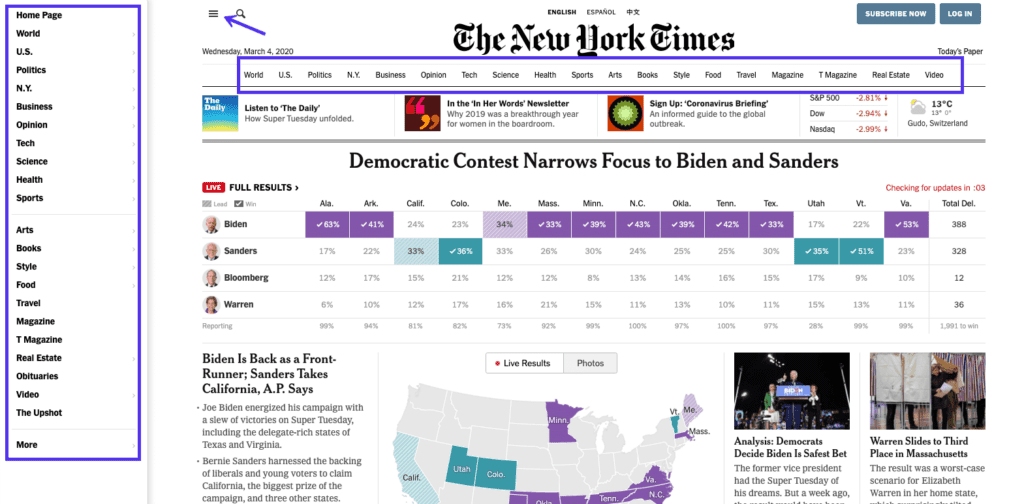
A navigational type of internal link work by allowing users to click through to different pages on the site.
An internal navigational link usually appears as menus or lists of links and can be found on every website page. In the site’s internal linking structure, they typically link to the essential pages on the site.
Navigational internal links help people move from one page to another and can be used to find specific pages or content within site.
Contextual links
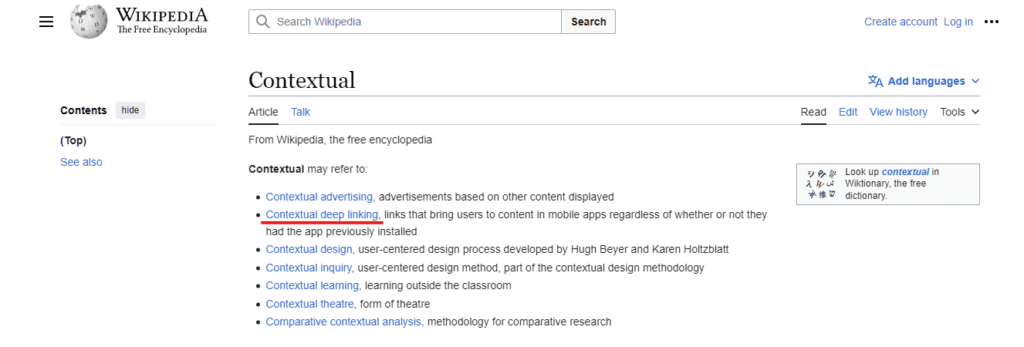
Contextual internal links are within the body of a website, and they provide additional information about the topic discussed.
These internal links are the most potent type of internal link, as they help search engines understand the relationship between the linked-to page and the linking page. A good rule is to only link to a page that makes sense to the content on the linking page.
Footer Links

Footer links appear in the footer of a website’s homepage.
Footer links are internal links pointing to pages that contain information about the website or company, such as the Contact page and About page.
These internal links are usually less important than the links found in the header or main body of the page but can still be helpful for visitors.
Footer links may include links to privacy policy pages and terms and conditions pages that are not as essential to the website’s main content.
Side Bar Links
Side bar links are a fundamental component of user interfaces, typically found in the form of a vertical column alongside the main content of a webpage or application. They serve as a navigational hub, offering users quick access to different sections or functionalities.
This design element is particularly effective in organising information hierarchically, with parent links leading to sub-links, creating an intuitive structure for users to explore.
To enhance usability, side bar links often incorporate visual elements such as icons alongside descriptive labels. These visual cues help in quick recognition and improve the overall user experience.
Additionally, side bars are commonly responsive, adapting their appearance on smaller screens by condensing into a menu or hamburger icon, ensuring a smooth experience across various devices. Customisation options allow developers to tailor the look and feel of side bar links to match the overall design theme of the website or application.
Why are internal Links Important for SEO?
An internal link is vital for search engine optimization (SEO) because they help link equity flow throughout your site structure, and they help improve the usability of your site.
When Google crawls a page, it follows linked pages. If there are many internal links, Google can easily find and index all the pages on your website.

An internal link is significant for websites with many pages because people often follow links to pages on your website when reading an article or blog post.
Internal links help Google navigate the website, and the spider will crawl. If there are multiple internal links, this can encourage people to explore your website further and visit more pages.
How does it affect SEO?

Internal and external links both improve your website’s SEO. However, external links are links pointing to other websites of your own, while internal links focus on links within your website.
Google Search Console is a service allowing you to view your website’s search traffic and performance.
When a webpage links to another webpage, it passes along credibility and page authority that can help improve that page’s ranking.
You can boost your website’s search engine results pages (SERPs) by linking to high-quality pages.
When choosing which pages to link to, look for those with relevance to your site’s topic and have high-quality content.
What are the benefits of Internal Links?
There are benefits to internal link building in your content. Here are just a few:
- It can improve user interaction
- It helps to spread the link juice
- Improve page rank and time on site
- It helps to crawl and indexing
It can improve user interaction
When users are satisfied with your content, they are more likely to stay on your website and click on pages linking to it.
When it comes to user experience, internal linking is essential. By providing links to other pages on your website, you can help guide your visitors to the information they need.
Additionally, it can also help boost your rankings in search engines if people are regularly clicking through your site.
It helps to spread the link juice
Internal linking is critical for SEO because it helps spread the link juice.
By linking to other internal subpages, you can pass on the authority or link juice to those pages, making them authoritative pages.
That’s why it’s essential to take internal linking opportunities and make sure that they pass link juice to the most critical pages on your site.
Dofollow links
Dofollow links are hyperlinks that pass linking power to the destination website. Giving linking power means that the destination website will boost its search engine rankings.
Dofollow internal links are essential for SEO because they help Google crawl and index your website.
When a website has dofollow internal links, it tells Google that the site is trustworthy and relevant. Search engines will follow the link to another page on your site when they crawl it.
Nofollow links
It’s essential to be aware of the nofollow internal links. These links don’t pass any linking power from one page to another.
Nofollow tag can be bad for your website because your pages are less likely to be found.
Nofollow internal links can still be helpful, though, as they can help send traffic to your site. Even if that traffic doesn’t improve your search engine ranking, it can still be valuable to your business or website.
Improve PageRank and Time on Site
You can help improve your PageRank if you add internal relevant links. By linking to other pages on your site, you effectively vouch for them and tell search engines they are worth paying attention to.
Adding internal links can help increase the amount of time people spend on your website or so-called “time on site”.
Finally, internal linking can also be a great usability tool. By linking to relevant pages, you can help guide visitors to the information they’re looking for.
Internal links can improve your website’s overall conversion rate and make it user-friendly.
It helps to crawl and indexing
Internal linking is a great way to help search engines crawl and index your website.
Linking to your content can be highly beneficial for SEO. It helps Google index and crawls your site, and it makes it more likely that Google will find your new content.
When you have internal links, you tell Google what your website is about and what is essential.
Internal links help Google understand your site and can result in higher rankings.

How to set up an internal linking strategy?
An internal linking strategy is key to a successful website. By linking to other pages on your site, you can help search engines and visitors navigate your site more easily.
If you want to set up a smart internal linking strategy, there are a few things you need to do:
- Recognize your important pages
- Do a site search
- Add contextual links
- Anchor Text
Recognize your important pages
When identifying the most important pages that should focus on your internal linking strategy, there are a few things to look for.
First, consider the page’s overall purpose and whether it is essential to your site’s operation. Suppose the page is necessary for visitors to navigate your website or find the information they’re looking for. In that case, it’s likely a vital page that you should include in your internal linking strategy.
Another critical factor to consider is the page’s popularity. If a particular page on your site receives a lot of traffic or has many backlinks, it’s also likely an essential page you’ll want to include in your internal linking strategy.
Finally, look at the page’s content and see if it contains any valuable or keyword-rich information that could help improve your site’s structure. If so, then this is another crucial factor to consider when determining which pages on your site are the most important and should focus on your internal linking strategy.
You can place posts in a specific hierarchy in a hierarchical post type by selecting a parent page. The parent page covers a category page (child page) and an overarching topically related theme. A parent page can have many child pages, but a child page can only have one parent page. So a child page can have a category page on the same level. For instance, a Team and Mission page is probably a child page of the About us page on a company website. And in that case, the Mission and Team pages are siblings.
Do a site search
Site search is a great way to find internal links relevant to the user’s query. By including a site search engine on your site, you can help users find the content they’re looking for and improve user experience.
If you’re unsure how to add a site search engine to your website, domain.comwill help. Once you’ve added a site search engine, you can start linking to other internal pages.
Site search can help you find content on your site, and you can also use it to help you publish new content. It enables you to see orphan pages not linked to from the home page.
Add contextual links
One of the essential things you can do is add contextual links to internal linking. These are links that appear in the body of your content, and they help provide readers with additional information about the topic at hand.
Search engines like Google use the links within your content to help determine your page’s topic and its relevance to a user’s query.
Anchor Text
You can ensure that your links are more valuable and informative for users and search engines by including descriptive anchor text.
Anchor texts are the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink. It’s essential to use the same anchor text that accurately describes the page you’re linking to. Use relevant terms for your anchor texts.
Anchor text is an essential keyword to include when optimizing for internal linking strategies. The exact match anchor text is the actual text in the link. It’s important not to over-optimize your internal link anchor text.
The maximum amount of anchor texts you can use in your internal linking strategy is eight keywords. So, make sure to keep your anchor text within this limit! Any more anchor text, and you risk being penalized by Google.
Add links to most recent posts
When crafting new content for your website, the incorporation of internal links plays a pivotal role in enhancing the user experience and bolstering the overall success of your site. By delving into the significance of integrating links into your latest posts or pages, we can unravel the various advantages of internal linking.
Firstly, the creation of a Relevant Content Network is established through internal links to recent posts. This network weaves a web of interconnected content, ensuring thematic cohesion and adhering to the concept of contextual links. This strategic approach not only benefits users by providing them with a seamless flow between related topics but also contributes to the overall organization and coherence of your site.
Secondly, internal links to recent posts are instrumental in elevating user engagement. The inclusion of such links encourages visitors to explore related topics, increasing the likelihood of discovering high-converting pages and thereby prolonging their engagement with your site. This intentional linking strategy fosters a sense of continuity and relevance, which is key to retaining user interest.
Moreover, the strategic addition of internal links goes beyond user engagement, positively impacting search engine visibility. This is achieved by contributing to a solid site structure, ultimately influencing search engine rankings through effective content indexing. The deliberate interconnection of content helps search engines recognize the thematic relevance and authority of your pages, enhancing your site’s position in search results.
Finally, by consistently linking to new posts, you mitigate the risk of creating orphan pages. This practice ensures that each page becomes an integral part of a cohesive structure, bolstering the overall value and coherence of your website. A structured internal linking strategy not only benefits users and search engines but also prevents the isolation of pages, contributing to a more unified and valuable online presence.
Add links to your taxonomies
Organizing your content into taxonomies, such as categories or tags, plays a pivotal role in enhancing the internal linking structure of your website. These taxonomies serve as a systematic way to categorize and group related content, contributing to a more organized and user-friendly site architecture.
By adding links to your taxonomies, you create a natural and effective internal linking system. This approach allows you to connect pages that share similar topics or themes, ensuring that users can seamlessly navigate between relevant pieces of content. This not only improves the overall user experience but also encourages visitors to explore more of your site, potentially leading them to high-converting pages.
Moreover, the use of taxonomies in internal linking has positive implications for search engine visibility. A well-organized taxonomy contributes to a solid site structure, making it easier for search engine crawlers to index and understand the content on your website. This, in turn, can positively impact your search engine rankings, as the interconnected nature of your content becomes more apparent to search algorithms.
Additionally, the incorporation of links within taxonomies aligns with effective keyword research, ensuring that the internal links are not only relevant but also contribute to the overall context of the linked pages. This relevance is essential for passing valuable link equity through internal links, benefiting the authority and ranking potential of the connected pages.
How to Audit Your Site’s Existing Internal Links
Auditing your site’s existing internal links is a crucial step in optimizing your website’s performance and ensuring a seamless user experience.
To conduct a thorough audit of your site’s existing internal links, begin by leveraging tools like Google Analytics and Search Console. These platforms provide essential data on your site’s current internal link structure, including reports on site links, internal link anchor text, and user behavior. Analyzing this information helps identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Next, assess your site’s architecture to understand the distribution and contribution of internal links to the overall structure. Pay particular attention to orphan pages—those lacking internal links—to ensure a cohesive user journey with all pages interconnected. This evaluation forms the foundation for a user-friendly site structure.
Evaluate the relevance of linked pages to the overarching theme and key topics of your site. Internal links should guide users to related and meaningful content, contributing to an intuitive navigation experience. Simultaneously, analyze the distribution of internal links across various pages, prioritizing high-converting and important content while avoiding link overload on less significant pages.
Take a close look at the anchor text used for internal links. Ensure consistency and diversity in anchor text, reflecting the content of the linked pages. Anchor text should be descriptive, providing users with a clear understanding of the linked content.
Consider the context in which internal links are placed to determine their value. Focus on providing valuable links that enhance the user experience and contribute to the overall site structure. Distinguish between nofollow and dofollow links, strategically allocating link equity to high-priority pages while maintaining a balanced approach.
Common Internal Link Problems & How to Fix Them
Internal linking is a crucial aspect of website optimization as it helps enhance the user experience, SEO performance, and overall site structure. While internal links help connect various pages within a website, giving smooth navigation for users and search engines, they are not without their challenges.
Common internal link problems can impact a site’s performance, affecting both user satisfaction and search engine rankings. We will explore some prevalent internal link issues and provide practical insights on how to address and rectify them, contributing to a more efficient and well-optimized online presence.
Over-Optimized Anchor Text:
Over-optimized anchor text is a common issue that can arise when website owners or SEO experts excessively use specific keywords in their internal links. While anchor text is vital for providing context to both users and search engines about the content of the linked page, Google and other search engines analyse over-optimized anchor text as a potential problem for several reasons:
Unnatural Linking Patterns:
- Overuse of exact-match anchor text can create unnatural linking patterns, signalling to search engines that the links may be manipulated for SEO purposes rather than reflecting organic user behaviour. Google’s algorithms are designed to detect patterns that deviate from natural, user-driven link structures.
Risk of Manipulation:
- Excessive optimization of anchor text can be perceived as an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. Google aims to provide users with the most relevant and genuine search results, and over-optimized anchor text may be seen as an attempt to artificially boost the perceived relevance of a page.
Potential for Penalties:
- Google’s algorithms are sophisticated and can identify websites employing manipulative SEO tactics. If a site is deemed to be excessively optimizing anchor text, it may face penalties, including a decrease in search engine rankings or even removal from search results. These penalties are part of Google’s efforts to maintain the integrity of its search results.
To address the issue of over-optimized anchor text, it’s advisable to follow these best practices:
Diversify Anchor Text:
- Use a variety of anchor text, including branded terms, generic phrases, and natural language that reflects the content of the linked page. This diversification appears more organic and aligns with natural linking behavior.
Focus on Relevance:
- Prioritize the relevance of the anchor text to the content it links to. Ensure that the text provides a clear and accurate description of the linked page’s topic, enhancing the user experience.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing:
- Avoid stuffing anchor text with keywords. Instead, focus on creating a balanced and user-friendly linking strategy that improves navigation and information flow on the website.
By addressing over-optimized anchor text and aligning internal linking practices with Google’s guidelines, website owners can enhance their site’s credibility and improve its standing in search engine results.
Broken Internal Links
Broken internal links can be a significant issue for a website, leading to a poor user experience and negatively impacting search engine optimization (SEO). Understanding how these links become problematic and implementing solutions is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functional website.
Over time, websites undergo updates, and content may be modified or removed. If internal links point to pages that no longer exist or have been altered, these links become broken.
When URLs are modified or restructured, internal links that still point to the old URLs become broken. This often happens during website migrations or redesigns.
If your site includes links to external content, those external pages may change or be removed, resulting in broken links on your site.
How to Fix Broken Internal Links:
Regular Audits:
- Solution: Schedule routine checks to identify and rectify broken links promptly. This proactive approach prevents users from encountering error pages and maintains a positive user experience.
301 Redirects:
- Solution: Redirect users and search engines to the updated or relevant content using 301 redirects. This ensures a seamless transition and preserves SEO value.
Custom 404 Pages:
- Solution: When users encounter a broken link, a well-designed 404 page can guide them back to relevant content. This improves user experience and helps them find the information they seek.
Utilize Webmaster Tools:
- Solution: Tools like Google Search Console can alert you to crawl errors, including broken internal links. Regularly check these reports and address any issues promptly.
Many Internal Links
Having too many internal links on a page can pose challenges for both user experience and search engine optimization.
An abundance of internal links on a page can overwhelm users, making it challenging for them to identify the most important or relevant content.
When a page contains numerous internal links, the value passed through each link can be diluted.
Excessive internal linking can signal to search engines that a page is trying to manipulate rankings.
Here’s an exploration of how an excessive number of internal links can become problematic and strategies to address this issue:
How to Fix the Problem of Too Many Internal Links:
Prioritize Important Pages:
- Solution: Identify and prioritize the most important pages that align with your site’s goals. Focus on linking to these pages strategically, providing users with a clear path to valuable content.
Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
- Solution: Opt for descriptive and contextually relevant anchor text rather than generic terms. This helps users and search engines understand the content of the linked page.
Audit and Streamline:
- Solution: Conduct regular audits of internal links on your pages. Remove links that no longer serve a purpose or are redundant. Streamline the number of links to maintain a focused and efficient linking structure.
Create Topic Clusters:
- Solution: Organize content into topic clusters, grouping related pages together. Use fewer, targeted internal links within each cluster, emphasizing the importance of thematic relevance.
User Testing:
- Solution: Conduct user testing to gauge the impact of internal linking on user experience. Gather feedback on whether users find the links helpful or if they feel overwhelmed. Adjust the number of links based on this feedback.
By addressing the issue of too many internal links through strategic prioritization, thoughtful anchor text usage, and regular audits, you can optimize both user experience and search engine performance. Balancing the quantity and quality of internal links ensures that each link serves its purpose effectively without overwhelming users or diluting SEO value.
Orphaned Pages
Orphaned pages, lacking internal links from other pages on the same website, can be problematic. These pages are isolated, making it challenging for users and search engines to discover and navigate to them. This isolation diminishes the visibility and value of the content on these pages.
How to Fix the Problem:
Internal Linking: Identify orphaned pages through website audits or tools like Google Analytics. Integrate relevant internal links from other pages to these orphans, connecting them to the broader site structure.
Site Navigation: Incorporate orphaned pages into the main site navigation, ensuring users can easily access them. This improves the overall user experience and encourages exploration of valuable content.
Sitemaps: Include orphaned pages in your website’s XML sitemap. This assists search engine crawlers in discovering and indexing these pages, enhancing their visibility in search engine results.
Related Content Sections: Add sections featuring related content on relevant pages. This not only aids in reducing orphaned pages but also enhances user engagement by guiding visitors to additional valuable information.
By addressing orphaned pages through strategic internal linking, site navigation improvements, sitemaps, and related content sections, you can ensure that every page contributes to the overall user experience and receives the attention it deserves from both users and search engines.
Inconsistent Linking Structure
Inconsistent linking structure refers to irregularities or discrepancies in the way internal links are implemented across a website. Search engines consider this a problem because a consistent and logical linking structure is important for understanding the hierarchy and relationships between different pages on a website. Inconsistencies in linking structure can lead to confusion for search engines and hinder their ability to accurately index and rank pages. Here’s how search engines perceive and address this issue:
Crawl Efficiency:
- Search engines use automated bots to crawl and index web pages. An inconsistent linking structure may result in a crawling error, where bots struggle to navigate the site’s pages systematically. This error can lead to incomplete indexing, affecting the visibility of certain pages in search results.
Page Importance and Authority:
- Consistent internal linking helps search engines determine the importance and authority of different pages. Inconsistent linking structures can mislead search engines into understanding which pages are more critical or relevant, impacting the distribution of authority throughout the site.
User Experience:
- Inconsistent linking structures can also impact the user experience. Users may find it challenging to navigate the website if the internal links do not follow a logical pattern. Poor user experience can contribute to higher bounce rates and lower engagement metrics, factors that search engines consider when evaluating the quality of a website.
To address the issue of inconsistent linking structure, consider the following solutions:
Create a Hierarchical Site Architecture:
- Develop a clear and hierarchical structure for your website. Group related content under relevant categories or sections, and ensure that the internal links reflect this hierarchy. This helps search engines understand the organisation of your content.
Standardise Linking Practices:
- Establish and adhere to consistent linking practices across the website. This includes using similar anchor text methods, maintaining a consistent number of internal links per page, and ensuring that navigation menus are uniform throughout the site.
Regularly Audit and Update Links:
- Conduct periodic audits of your website’s internal links to identify any inconsistencies. Update links as the site evolves, ensuring that new pages are appropriately linked and outdated or broken links are addressed promptly.
Use Sitemaps:
- Implement XML sitemaps to provide search engines with a comprehensive overview of your site’s structure. Sitemaps can help search engine bots discover and index pages more efficiently, reducing the impact of inconsistent linking structures.
By addressing inconsistent linking structures, website owners can enhance both search engine visibility and the user experience, contributing to improved rankings and overall site performance.
FAQs
How many internal links should I include per post?
Include 2–5 internal links per post that relate to the content and boost the user experience. Use quality links that provide additional value to readers and align with the overall structure of your website. Avoid overloading posts with links, and regularly review and update your internal linking strategy for optimal effectiveness.
Should I add internal links to my pages with more or less traffic?
Yes, add internal links to both high-traffic and low-traffic pages. On high-traffic pages, focus on enhancing user experience by linking to related content. While using higher-traffic pages to boost visibility and increase the chances of being indexed in search engines works better for low-traffic pages. This balanced strategy benefits user engagement and overall site structure.
Are internal links backlinks?
No, internal links are not considered backlinks. Internal links connect different pages within the same website and establish relationships between content. Meanwhile, backlinks, or inbound links, are links from external websites pointing to your site. While both internal links and backlinks are important for SEO, they serve different purposes: internal links boost site structure and user navigation, while backlinks contribute to a website’s authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, internal linking is crucial for website success. Building a Relevant Content Network through links to recent posts enhances user experience and boosts SEO. Strategic internal linking encourages user exploration, prevents orphan pages, and provides a clear path for search engine crawlers.
Understanding the differences between internal and external links is vital, as they serve distinct purposes in site architecture and search engine rankings. Various types of internal links, such as navigational and contextual links, improve user interaction and site visibility.
Regular audits help address common issues like over-optimized anchor text and broken links, optimizing user experience. Issues like too many internal links or orphaned pages can be resolved by prioritizing important pages and incorporating them into site navigation.
Finding opportunities for new pages involves audience research, competitor analysis, keyword research, and staying informed about industry trends. This proactive approach keeps the website dynamic and responsive to audience needs.









