AI automation tools are software platforms that use artificial intelligence to automate tasks and decisions that go beyond fixed, rule-based workflows. These tools analyse data, recognise patterns, and adapt actions based on context and outcomes. Businesses use AI automation tools to handle decision-heavy operations such as orchestration, prioritisation, autonomous task execution, and system-level automation across teams and platforms.
Unlike traditional workflow automation, which relies on predefined triggers and linear rules, AI automation introduces learning and prediction into operational processes. This enables automation to function in environments with unstructured data, variable inputs, and changing conditions. As organisations scale and operational complexity increases, AI automation tools act as coordination layers, guiding how work progresses rather than simply executing repetitive steps.
What AI Automation Tools Are and How They Extend Beyond Workflow Automation
AI automation tools operate as decision-enabled systems rather than simple task executors. They process signals from data sources, systems, and user behaviour to determine which actions should occur, when, and how they should be executed. This allows businesses to automate outcomes rather than only automating individual steps.
AI automation tools are designed to handle complexity that static workflows cannot manage, including:
- Interpreting structured and unstructured data such as text, usage signals, and behavioural inputs
- Prioritising actions based on context rather than fixed rules
- Adapting execution paths when conditions change
- Coordinating decisions across multiple systems and teams
Workflow automation software focuses on predictable task flows such as approvals, routing, and scheduled actions. AI automation tools extend this capability by managing uncertainty, prioritisation, and judgement-based execution. They function effectively in environments where inputs vary, and outcomes cannot be defined in advance. For this reason, workflow automation represents only one subset within the broader AI automation landscape.
Core Categories of AI Automation Tools Used by Businesses
AI automation tools fall into distinct system roles based on how they automate decisions and execution. Understanding these categories helps businesses select platforms that align with operational complexity rather than feature count.
The main categories of AI automation tools used by businesses include:
- Workflow and app integration automation for coordinating actions across software platforms
- Enterprise robotic process automation for system-level and compliance-driven processes
- AI agents for autonomous task execution and decision handling
- AI content and knowledge automation for cognitive and information-based work
- Open-source or developer-controlled automation systems for infrastructure-level control
Each category supports different levels of decision depth, governance, and scalability. By identifying the role automation should play in operations, businesses can select tools that support long-term reliability rather than short-term convenience.
1. Zapier
Category: AI-Enhanced Workflow and Decision Routing
Zapier operates as a coordination layer that connects thousands of applications while introducing AI-assisted routing and logic into automation flows. Beyond simple trigger-action workflows, Zapier supports conditional logic, AI steps, and dynamic decision routing that adapt based on data inputs. This allows teams to automate decisions such as lead prioritisation, content handling, and task distribution.
Zapier suits businesses that want to extend existing workflows with intelligence rather than rebuild systems. Its value lies in orchestration across tools while maintaining simplicity, making it effective for operational teams managing cross-platform processes that require adaptive handling rather than static execution.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Free | 0 | Single-step automations, core apps | Very low task limits |
| Starter | 19.99 | Multi-step Zaps, premium apps | Task limits scale quickly |
| Professional | 49 | Advanced logic, webhooks | Cost increases with volume |
| Team | 69 | Shared workspaces, permissions | Task-based pricing remains |
| Enterprise | Custom | Security and admin controls | Pricing not public |
2. Make (formerly Integromat)
Category: Advanced AI-Assisted Workflow Orchestration
Make supports complex orchestration by combining visual workflow design with data transformation and AI-assisted logic. It allows businesses to design multi-branch scenarios that react dynamically to data conditions and processing outcomes. This enables decision-driven automation across operations, finance, marketing, and technical workflows.
Make is used when automation requires visibility and control across multiple decision points. Its operation-based pricing and modular structure suit teams that manage complex logic while maintaining transparency over how automation behaves under different conditions.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Free | 0 | Basic scenarios, limited operations | Not production-ready |
| Core | 9 | Higher operation limits | Complex logic consumes usage |
| Pro | 16–29 | Advanced modules, scheduling | Requires usage monitoring |
| Teams | 34+ | Collaboration features | Scales with team size |
| Enterprise | Custom | High-volume orchestration | Custom contracts |
3. Microsoft Power Automate
Category: Ecosystem-Level AI and Enterprise Automation
Microsoft Power Automate functions as an automation layer within the Microsoft ecosystem, combining workflow automation, AI Builder capabilities, and robotic process automation. It enables businesses to automate decisions across documents, systems, and user interactions while maintaining governance and compliance controls.
Power Automate suits organisations that operate heavily within Microsoft environments. Its strength lies in enterprise integration, identity management, and AI-assisted processing of documents and data, making it effective for system-level automation rather than isolated task flows.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Per User | 15 | Cloud flows, standard connectors | Limited RPA features |
| Per Flow | 100 | Organisation-wide flows | Requires careful design |
| RPA add-on | 150 | Desktop automation | Windows dependency |
| Premium | Included in M365 tiers | AI Builder, premium connectors | Feature gating by licence |
4. n8n
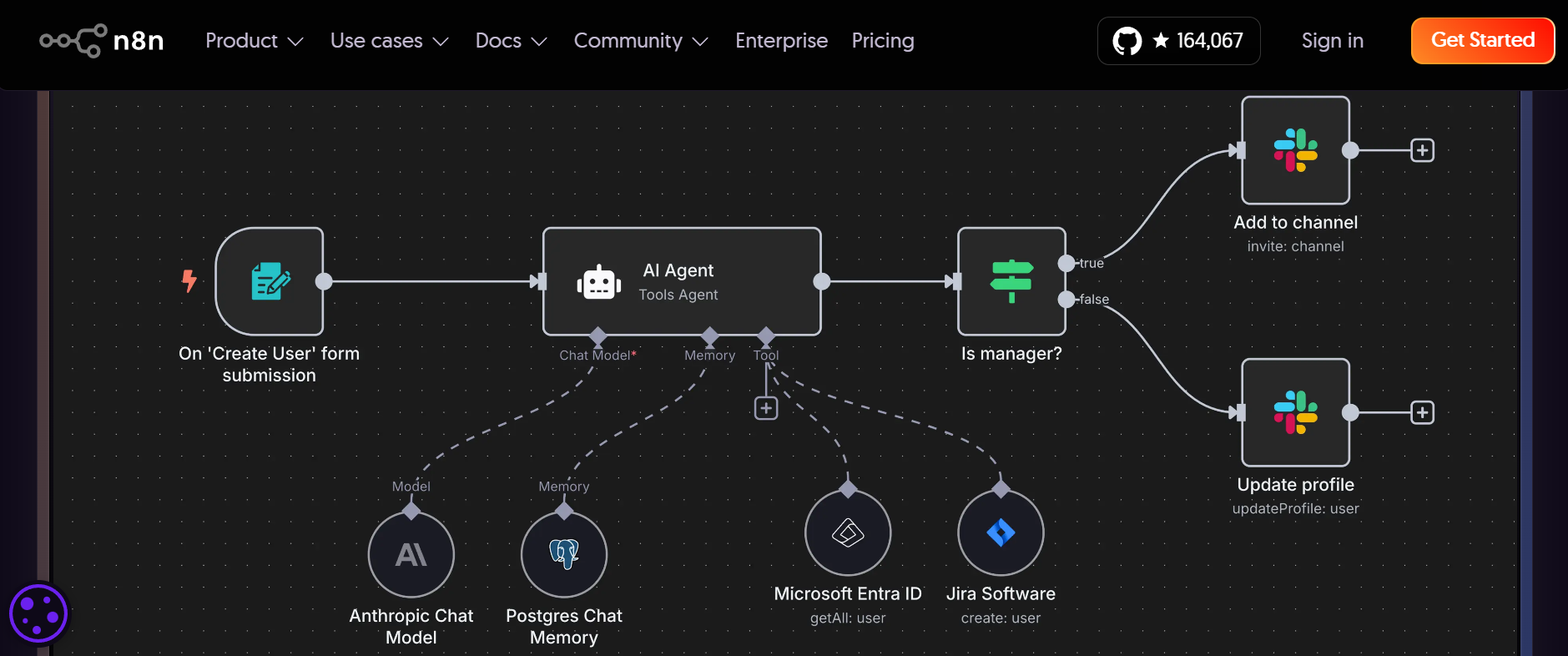
Category: Open-Source and Developer-Controlled AI Automation
n8n provides infrastructure-level automation with full control over logic, data handling, and deployment. It supports AI-assisted workflows, API-driven execution, and complex conditional logic, while enabling businesses to self-host their automation infrastructure. This model suits organisations that require ownership, transparency, and long-term cost predictability.
n8n is used when deep integration with internal systems or custom logic is required. Its open-source approach allows teams to design automation into the system architecture rather than relying on third-party constraints.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Self-hosted | 0 | Full control, unlimited workflows | Requires infrastructure |
| Cloud Starter | 20–24 | Managed hosting | Execution limits |
| Cloud Pro | 50–60 | larger scale and resources | Usage-based scaling |
| Business | Custom | Team and governance features | Quote required |
| Enterprise | Custom | Compliance and security controls | Technical overhead |
5. UiPath

Category: Enterprise AI and Robotic Process Automation
UiPath specialises in automating system-level processes using AI-assisted robotic automation. It enables businesses to automate tasks across legacy systems, structured applications, and documents while applying machine learning to improve accuracy and decision handling. This makes UiPath suitable for environments with high volume, compliance requirements, and operational risk.
UiPath is commonly used in finance, operations, and regulated industries where automation must replicate and enhance human system interactions. Its focus lies on reliability, governance, and scale rather than rapid experimentation.
Pricing overview
| Package | Price | Key features | Limitations |
| Automation Cloud | Custom | Cloud RPA and AI features | Enterprise commitment |
| Studio | Custom | Bot development tools | Requires training |
| Attended RPA | Custom | Human-in-loop automation | Higher setup cost |
| Unattended RPA | Custom | Full automation at scale | Infrastructure planning |
6. Lindy
Category: AI Agents and Autonomous Task Execution
Lindy represents a newer automation paradigm based on AI agents that execute tasks autonomously. These agents handle activities such as scheduling, communication, research, and coordination without predefined workflows. They operate by interpreting instructions, context, and outcomes rather than following static logic.
Lindy suits businesses exploring task automation that resembles human execution rather than system orchestration. Its value lies in reducing manual handling of repetitive knowledge work while maintaining adaptability across changing conditions.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Free | 0 | Limited agents and tasks | Very restricted usage |
| Starter | From ~30 | Task-specific AI agents | Feature caps |
| Pro | From ~100 | Advanced agent logic | Scaling cost |
| Business | Custom | Multi-agent workflows | Sales-led pricing |
7. ChatGPT (OpenAI)
Category: AI Content, Reasoning, and Knowledge Automation
ChatGPT serves as a general-purpose automation layer for content creation, analysis, and reasoning. Businesses use it to automate drafting, summarisation, data interpretation, and internal knowledge handling. While it does not execute workflows natively, it automates cognitive work that traditionally required human input.
ChatGPT fits organisations that need flexible automation across writing, research, and analysis. Its effectiveness depends on structured usage and governance, particularly when integrated into broader operational systems.
Pricing plans and limitations
| Plan | Price (USD/month) | Key features | Limitations |
| Free | 0 | Basic AI assistance | Usage limits |
| Plus | 20 | Advanced models and tools | Not enterprise-grade |
| Team | 25–30 per user | Collaboration and admin tools | Per-seat pricing |
| Enterprise | Custom | Security and data controls | Contract required |
How Businesses Should Choose AI Automation Tools Beyond Workflows
Businesses should evaluate AI automation tools based on decision complexity, data structure, and governance needs. These platforms influence how work is prioritised and executed, so suitability depends on operational maturity rather than feature breadth.
Key factors to consider include the scope of automation, level of autonomy, data readiness, team capability, and cost predictability. Clear alignment between system roles and business needs reduces operational risk and ensures that automation supports long-term scalability.
AI Automation Tools by System Role
| Tool | Primary system role | Best suited for |
| Zapier | Cross-app orchestration | Multi-tool operations |
| Make | Logic-heavy orchestration | Complex workflows |
| Power Automate | Ecosystem automation | Microsoft environments |
| n8n | Infrastructure automation | Technical teams |
| UiPath | System-level automation | Regulated operations |
| Lindy | Autonomous task agents | Knowledge work |
| ChatGPT | Cognitive automation | Content and analysis |
Conclusion
AI automation tools enable businesses to automate decisions, execution, and coordination beyond the limits of rule-based workflows. These platforms operate as systems that guide how work progresses rather than simply replacing manual steps. By understanding system roles and the scope of automation, organisations can select tools that support operational clarity and controlled scalability.
As business environments grow more complex, AI automation becomes an operational capability rather than a technical enhancement. Choosing the right tools requires alignment between decision depth, governance requirements, and long-term objectives. When implemented with intent, AI automation tools support sustainable efficiency and resilience in 2026 and beyond.









